|
Template matching with basis image reconstruction
and its image registration applications
Student
: Tzu-Hsun Tseng
Advisor : Dr. Du-Ming Tsai
Department
of Industrial Engineering and Management
YUAN-ZE University
ABSTRACT
Template matching is a technique to find
the instance of a template in an image. Template matching techniques are
traditionally based on Image Difference and Normalized Cross Correlation.
They are very sensitive to slight changes in rotation and scale. In this
study, a basis image reconstruction method that can tolerate geometric
changes is developed for template matching. To use the basis image
reconstruction, a number of template patches with most representative
patterns are first manually or automatically selected from a reference image.
The templates then form the basis images. In the matching process, a windowed
subimage of the template size is constructed by the linear combination of the
basis images. Two measurement indicators are used to evaluate the similarity
between two compared subimages. First, the coefficients of the linear
combination of the basis images are used as the feature vector. The Euclidean
distance between the feature vectors of the original template and the test
subimage quantifies the similarity score. The second indicator is the gray
level difference of the test subimage and its reconstruction. Experimental
results show that the basis image reconstruction method is 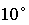 in rotation and
10% in scale changes. By including templates with larger rotational angles in
the basis images, the proposed method can further identify objects with
severe direction changes. in rotation and
10% in scale changes. By including templates with larger rotational angles in
the basis images, the proposed method can further identify objects with
severe direction changes.
The applications of the proposed
template matching technique in this study are industrial calibration and the
detection of moving objects (intruders) from a mobile robot. For industrial
calibration, it can be applied in positioning and calibrating a workpiece so
that the assembly failure or inspection error can be reduced. For security
robots, the proposed technique can align two consecutive images in the video
sequence due to the shaking of the camera. Then the simple image differencing
can effectively and efficiently segment the moving objects from the
background. In the experiment, an image of size 160 120 pixels needs only 0.031 seconds of processing time. The
template matching technique proposed in this study can be used for real-time
applications. 120 pixels needs only 0.031 seconds of processing time. The
template matching technique proposed in this study can be used for real-time
applications.
Keywords:
Template matching; Basis image reconstruction; Image registration; Security
robot.
|